The Islamic view of Jesus lies between two extremes. The Jews , who rejected Jesus as a Prophet of God, called him an impostor. The Christians, on the other hand, considered him to be the son of God and worship him as such. Islam considers Jesus to be one of the great prophets of God and respects him as much as Ibrahim (Abraham), Moses, and Mohammed. (Peace Be Upon Them) This is conformity with the Islamic view of the oneness of God, the oneness of Divine guidance, and the complementary role of the subsequent mission of God's messengers.
The essence of Islam - willing submission to the will of God - was revealed to Adam, who was passed it on to his children. All following revelations to Noah, Ibrahim, Moses, Jesus, and finally Mohammed (Peace Be Upon Them) were conformity with that message, with some elaboration to define the revelation between man and God, man and man, man and instructions. Thus, any contradictions among revealed religions is viewed by Islam as a man-made element introduced into these religions. The position of Jesus in the three major religions - Judaism, Christianity, and Islam - should not be an exception.
Although the Quran does not present a detailed life-story of Jesus, it highlights the important aspects of his birth, his mission, his ascension to heaven, and passes judgements on the Christian beliefs concerning him. The Quranic account of Jesus starts with the conception of his mother, Mary, whose mother, the wife of Imran, vowed to dedicate her child to the service of God in the temple. When Mary became a woman, the Holy Spirit (the Archangel Gabriel) appeared to her as a man bringing her news of a son. We read the following dialogue in the Quran between Mary and the Angel:
"When the angel said, "Mary, god gives you a good tidings of a Word from Him whose name is messiah, Jesus, son of Mary, -high honoured shall he be in this world and the next, near stationed to God. He shall speak to men in the cradle, and of age, and righteous he shall be, "lord" said Mary "How shall I have a son, seeing no mortal has touched me? "Even so, he said "God creates what He will".
 One of the reasons that the Islamic family works is because of its clearly defined structure, where each member of the household knows his or her role. The Prophet Muhammad, may the mercy and blessings of God be upon him, said:
One of the reasons that the Islamic family works is because of its clearly defined structure, where each member of the household knows his or her role. The Prophet Muhammad, may the mercy and blessings of God be upon him, said:
 In Islam, considering the well-being of the “other” instead of just the “self” is a virtue so rooted in the religion that it is evident even to those outside it. The British humanitarian and civil rights lawyer, Clive Stafford-Smith, a non-Muslim, stated: “What I like about Islam is its focus on the group, which is opposite to the West’s focus on individuality.”
In Islam, considering the well-being of the “other” instead of just the “self” is a virtue so rooted in the religion that it is evident even to those outside it. The British humanitarian and civil rights lawyer, Clive Stafford-Smith, a non-Muslim, stated: “What I like about Islam is its focus on the group, which is opposite to the West’s focus on individuality.”
 Few centuries before Jesus the outstanding Greek civilizationcame to exist, bringing into the world such knowledgeable minds as Aristotle, Euclid, Socrates, Galen and Ptolemy. Their contributions to philosophy, mathematics, geography, astronomy and medicine became the corner stone of modern science.
Few centuries before Jesus the outstanding Greek civilizationcame to exist, bringing into the world such knowledgeable minds as Aristotle, Euclid, Socrates, Galen and Ptolemy. Their contributions to philosophy, mathematics, geography, astronomy and medicine became the corner stone of modern science. In the early 7th century, the two most powerful empires at the time were the Byzantine
In the early 7th century, the two most powerful empires at the time were the Byzantine Iron is one of the elements highlighted in the Quran. In the chapter known Al-Hadeed, meaning Iron, we are informed:
Iron is one of the elements highlighted in the Quran. In the chapter known Al-Hadeed, meaning Iron, we are informed: Modern Science has discovered that in the places where two different seas meet, there is a barrier between them. This barrier divides the two seas so that each sea has its own temperature, salinity, and density.
Modern Science has discovered that in the places where two different seas meet, there is a barrier between them. This barrier divides the two seas so that each sea has its own temperature, salinity, and density.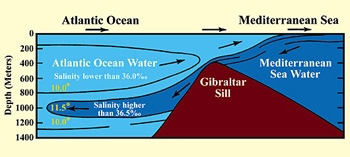
 The science of modern cosmology, observational and theoretical, clearly indicates that, at one point in time, the whole universe was nothing but a cloud of ‘smoke’ (i.e. an opaque highly dense and hot gaseous composition).
The science of modern cosmology, observational and theoretical, clearly indicates that, at one point in time, the whole universe was nothing but a cloud of ‘smoke’ (i.e. an opaque highly dense and hot gaseous composition).